Functions: Storage and Verification¶
initialize¶
Initializes BTC-Relay with the first Bitcoin block to be tracked and initializes all data structures (see Data Model).
Note
BTC-Relay does not have to be initialized with Bitcoin’s genesis block! The first block to be tracked can be selected freely.
Warning
Caution when setting the first block in BTC-Relay: only succeeding blocks can be submitted and predecessors will be rejected!
Specification¶
Function Signature
initialize(blockHeaderBytes, blockHeight)
Parameters
relayer: the account submitting the blockblockHeaderBytes: 80 byte raw Bitcoin block headerblockHeight: integer Bitcoin block height of the submitted block header
Events
Initialized(blockHeight, blockHash, relayer): if the first block header was stored successfully, emit an event with the stored block’s height (blockHeight) and the (PoW) block hash (blockHash).
Errors
ERR_ALREADY_INITIALIZED = "Already initialized": return error if this function is called after BTC-Relay has already been initialized.
Preconditions¶
- This is the first time this function is called, i.e., when BTC-Relay is being deployed.
Function sequence¶
Check if
initializeis called for the first time. ReturnERR_ALREADY_INITIALIZEDif BTC-Relay has already been initialized.Parse
blockHeaderBytes, extracting themerkleRoot(extractMerkleRoot),timestamp(extractTimestamp) andtarget(extractNBits and nBitsToTarget) fromblockHeaderBytes, and compute the block hash (hashCurrentBlock) using sha256d (passingblockHeaderBytesas parameter).Create a new
BlockChainentry inChains:chainId =incrementChainCounterstartHeight = blockHeightmaxHeight = blockHeightnoData = Vec::new()invalid = Vec::new()- Insert
hashCurrentBlockin thechainmapping usingblockHeightas key.
Insert a pointer to
BlockChainintoChainsIndexusingchainIdas key.Store a new
RichBlockHeaderstruct containingmerkleRoot,blockHeight,timestamp,target, and a pointer (chainRef) to theBlockChainstruct - as associated with this block header - inBlockHeaders, usinghashCurrentBlockas key.Set
BestBlock = hashCurrentBlockandBestBlockHeight = blockHeight.Emit a
Initializedevent usingheightandhashCurrentBlockas input.
Warning
Attention: the Bitcoin block header submitted to initialize must be in the Bitcoin main chain - this must be checked outside of the BTC Bridge before making this function call! A wrong initialization will cause the entire BTC Bridge to fail, since verification requires that all submitted blocks must (indirectly) point to the initialized block (i.e., have it as ancestor, just like the actual Bitcoin genesis block).
storeBlockHeader¶
Method to submit block headers to the BTC-Relay. This function calls verifyBlockHeader providing the 80 bytes Bitcoin block header as input, and, if the latter returns True, extracts from the block header and stores the hash, height and Merkle tree root of the given block header in BlockHeaders.
If the block header extends an existing BlockChain entry in Chains, it appends the block hash to the chains mapping and increments the maxHeight. Otherwise, a new Blockchain entry is created.
Specification¶
Function Signature
storeBlockHeader(relayer, blockHeaderBytes)
Parameters
relayer: the account submitting the blockblockHeaderBytes: 80 byte raw Bitcoin block header.
Events
StoreMainChainHeader(blockHeight, blockHash, relayer): if the block header was successful appended to the currently longest chain (main chain) emit an event with the stored block’s height (blockHeight) and the (PoW) block hash (blockHash).StoreForkHeader(forkId, blockHeight, blockHash, relayer): if the block header was successful appended to a new or existing fork, emit an event with the block height (blockHeight) and the (PoW) block hash (blockHash).
Preconditions¶
- The BTC Bridge status must not be set to
SHUTDOWN: 3.
Warning
The BTC-Relay does not necessarily have the same view of the Bitcoin blockchain as the user’s local Bitcoin client. This can happen if (i) the BTC-Relay is under attack, (ii) the BTC-Relay is out of sync, or, similarly, (iii) if the user’s local Bitcoin client is under attack or out of sync (see Security Analysis).
Note
The 80 bytes block header can be retrieved from the bitcoin-rpc client by calling the getBlock and setting verbosity to 0 (getBlock <blockHash> 0).
Function sequence¶
Call verifyBlockHeader passing
blockHeaderBytesas function parameter. If this call returns an error , then abort and return the raised error. If successful, this call returns a parsedBlockHeader(BlockHeader) struct.Determine which
BlockChainentry inChainsthis block header is extending, or if it is a new fork and hence a newBlockChainentry needs to be created. For this, get theprevBlockHeader(RichBlockHeader) stored inBlockHeaderswithBlockHeader.hashPrevBlockand useprevBlockHeader.chainRefto lookup the associatedBlockChainstruct inChainsIndex. Then, check if theprevBlockHeader.blockHeight(as referenced byhashPrevBlock) is equal toBlockChain.maxHeight.- If not equal (can only be less in this case), then the current submission is creating a new fork.
i ) Create a new
BlockChainstruct, settingBlockChain.startHeight = RichBlockHeader.blockHeight(as referenced inhashPrevBlock),BlockChain.maxHeight = RichBlockHeader.blockHeight + 1(as referenced inhashPrevBlock), and appendinghashCurrentBlock(compute the block hash using sha256d, passingblockHeaderBytesas parameter) to the (currently empty)BlockChain.chainmapping.ii ) Set
BlockChain.chainId =incrementChainCounter.iii ) Insert the new
BlockChainintoChains.iv ) Insert the new
BlockChainintoChainsIndexusingBlockChain.chainIdas key.
- Otherwise, if equal, then the current submission is extending the
BlockChainreferenced byRichBlockHeader.chainRef(as per``hashPrevBlock``).i ) Append the
hashCurrentBlockto thechainmap inBlockChainand incrementmaxHeightii ) Check if a blockchain reorganization is necessary. For this, call checkAndDoReorg passing the pointer to
BlockChainas parameter.
- Check if
BlockChainis the main chain, i.e. check ifchainId == MAIN_CHAIN_ID.- If
BlockChainis not the main chain (chainId =/= MAIN_CHAIN_ID) andBlockChain.maxHeight > nextBestForkHeightsetnextBestForkHeight = BlockChain.maxHeight. - If
BlockChainis the main chain (chainId == MAIN_CHAIN_ID) setBestBlock = hashCurrentBlockandBestBlockHeight = BlockChain.maxHeight.
- If
- Create a new
RichBlockHeaderand initalize as follows:
RichBlockHeader.blockHeight = prevBlock.blockHeight + 1,RichBlockHeader.chainRef = BlockChain.chainId,RichBlockHeader.merkleRoot = BlockHeader.merkleRoot,RichBlockHeader.target = BlockHeader.target,RichBlockHeader.timestamp = BlockHeader.timestamp,RichBlockHeader.hashPrevBlock = BlockHeader.hashPrevBlock
- Insert
RichBlockHeaderintoBlockHeadersusinghashCurrentBlockas key. - Emit event.
- If submission was to main chain (
BlockChainwithchainId == MAIN_CHAIN_ID), emitStoreMainChainBlockHeaderevent usingheightandhashCurrentBlockas input (StoreMainChainHeader(height, hashCurrentBlock)). - If submission was to another
BlockChainentry (new or existing), emitStoreForkHeader(height, hashCurrentBlock).
- If submission was to main chain (
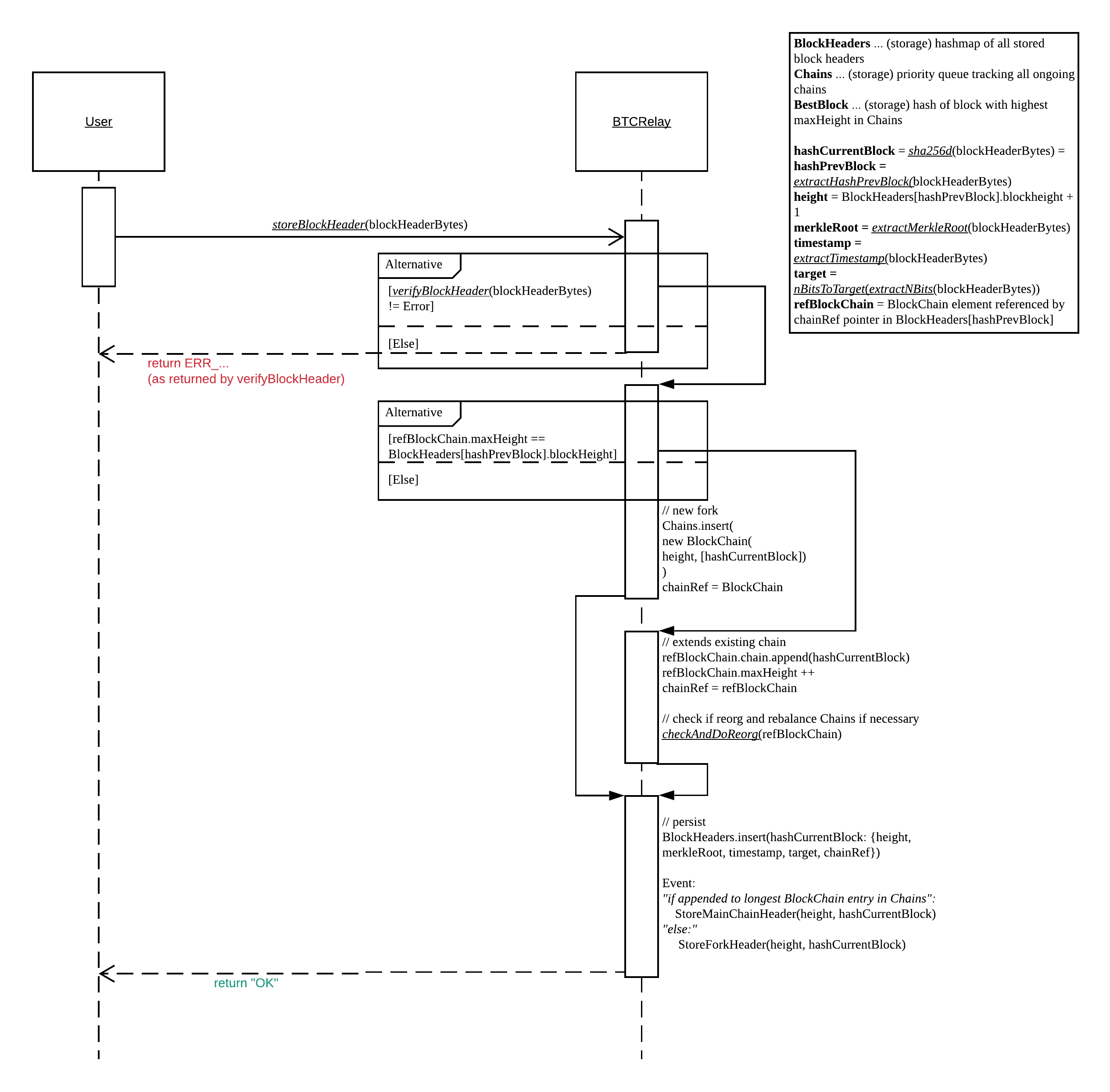
Sequence diagram showing the function sequence of storeBlockHeader.
checkAndDoReorg¶
This function is called from storeBlockHeader and checks if a block header submission resulted in a chain reorganization.
Updates the ordering in / re-balances Chains if necessary.
Specification¶
Function Signature
checkAndDoReorg(fork)
Parameters
&fork: pointer to aBlockChainentry inChains.
Events
ChainReorg(newChainTip, blockHeight, forkDepth): if the submitted block header on a fork results in a reorganization (fork longer than current main chain), emit an event with the block hash of the new highest block (newChainTip), the new maximum block height (blockHeight) and the depth of the fork (forkDepth).
Function Sequence¶
- Check if the ordering of the
BlockChainentry needs updating. For this, check themaxHeightof the “next-highest”BlockChain(parent in heap or predecessor in sorted linked list) inChains.
- If
forkis the top-level element, i.e., the main chain, do nothing.- Else if the “next-highest” entry has a lower
maxHeight, update ordering by switching positions - continue, until reaching the “top” of theChainsdata structure or aBlockChainentry with a highermaxHeight.
- If ordering was updated, check if the top-level element in the
Chainsdata structure changed (i.e., is no longer the main chain defined byMAIN_CHAIN_ID). If this is the case:
- Retrieve the main chain
BlockChainentry (mainChain) fromChainsIndexusingMAIN_CHAIN_ID- Check if the
maxHeightof the new top-levelBlockChainexceedsmainChain.maxHeightby at leastSTABLE_BITCOIN_CONFIRMATIONS. If true, continue. If false,return(no chain reorg needs to be executed yet).
- Create a new empty
BlockChain(forkedMainChain) struct and initalize with:
forkedMainChain.chainId =incrementChainCounter,forkedMainChain.chain = HashMap::new()forkedMainChain.startHeight = fork.startHeight,forkedMainChain.maxHeight = mainChain.maxHeightforkedMainChain.noData = Vec::new()forkedMainChain.invalid = Vec::new()
- Loop: starting from
fork.startHeightascurrHeightuntilfork.maxHeight:i ) Set
forkedMainChain.chain[currHeight] = mainChain.chain[currHeight](overwrite the forked out main chain blocks with blocks in the fork).ii ) Get the
RichBlockHeaderfor the newmainChain.chain[currHeight]and update itschainRefto point tomainChain.iii ) Set
forkedMainChain.chain[currHeight] = fork.chain[currHeight](write forked main chain blocks to newBlockChainentry to be tracked as an ongoing fork).iv ) Get the
RichBlockHeaderfor the newforkedMainChain.chain[currHeight]and update itschainRefto point toforkedMainChain.v ) If
currHeight > mainChain.maxHeightsetmainChain.maxHeight = currHeight.
- For each block height in
fork.noDataandfork.invalid: add the block height tomainChain.noDataandmainChain.noDatarespectively.- Update
BestBlockHeight = mainChain.maxHeightandBestBlock = mainChain.chain[mainChain.maxHeight](nextBestForkHeightupdated in storeBlockHeader).
- Check that
noDataorinvalidare both empty inmainChain. If this is the case, check if we need to update the BTC Bridge state.i ) If
noDataorinvalidare both empty andErrorsin Security Analysis containsNO_DATA_BTC_RELAYorINVALID_BTC_RELAYcallrecoverFromBTCRelayFailureto recover the BTC Bridge from the BTC-Relay related error.ii ) If
BridgeStatusis set toRUNNINGand eithernoDataorinvalidare not empty in the new main chainBlockChainentry: updateBridgeStatustoERRORand appendNO_DATA_BTC_RELAYorINVALID_BTC_RELAY(depending on which ofinvalidandnoDatalists was not empty) to theErrorslist.
- Remove
forkfromChains.- Emit a
ChainReorg(newChainTip, blockHeight, forkDepth), wherenewChainTipis the newBestBlock,blockHeightis the newBestBlockHeight, andforkDepthis the depth of the fork (fork.maxHeight - fork.startHeight).
Note
We may want to track the mainChain identifier separately for quicker access (same main chain updated in case of forks).
verifyBlockHeader¶
The verifyBlockHeader function parses and verifies Bitcoin block headers.
If all checks are successful, returns a BlockHeader representation of the 80 byte raw block header given as input.
Note
This function does not check whether the submitted block header extends the main chain or a fork. This check is performed in storeBlockHeader.
Specification¶
Function Signature
verifyBlockHeader(blockHeaderBytes)
Parameters
blockHeaderBytes: 80 byte raw Bitcoin block header.
Returns
BlockHeader: if all checks pass successfully, return a parsedBlockHeader.
Errors
ERR_DUPLICATE_BLOCK = "Block already stored": return error if the submitted block header is already stored in BTC-Relay (duplicate PoWblockHash).ERR_PREV_BLOCK = "Previous block hash not found": return error if the submitted block does not reference an already stored block header as predecessor (viaprevBlockHash).ERR_LOW_DIFF = "PoW hash does not meet difficulty target of header": return error when the header’sblockHashdoes not meet thetargetspecified in the block header.ERR_DIFF_TARGET_HEADER = "Incorrect difficulty target specified in block header": return error if thetargetspecified in the block header is incorrect for its block height (difficulty re-target not executed).
Function Sequence¶
- Call parseBlockHeader passing
blockHeaderBytesas parameter to parse the block header. If this call returns an error, abort and return the error. If successful, parseBlockHeader returns a parsedBlockHeader(BlockHeader) struct. - Compute
hashCurrentBlock, the double SHA256 hash over the 80 bytes block header, using sha256d (passingblockHeaderBytesas parameter). - Check that the block header is not yet stored in BTC-Relay (
hashCurrentBlockmust not yet be inBlockHeaders). ReturnERR_DUPLICATE_BLOCKotherwise. - Get the
RichBlockHeader(prevBlock) referenced by the submitted block header viaBlockHeader.hashPrevBlock. ReturnERR_PREV_BLOCKif no such entry was found. - Check that the Proof-of-Work hash (
hashCurrentBlock) is below theBlockHeader.target. ReturnERR_LOW_DIFFotherwise. - Check that the
BlockHeader.targetis correct by calling checkCorrectTarget passingBlockHeader.hashPrevBlock,prevBlock.blockHeightandBlockHeader.targetas parameters (as per Bitcoin’s difficulty adjustment mechanism, see here). If this call returnsFalse, returnERR_DIFF_TARGET_HEADER. - Return
BlockHeader
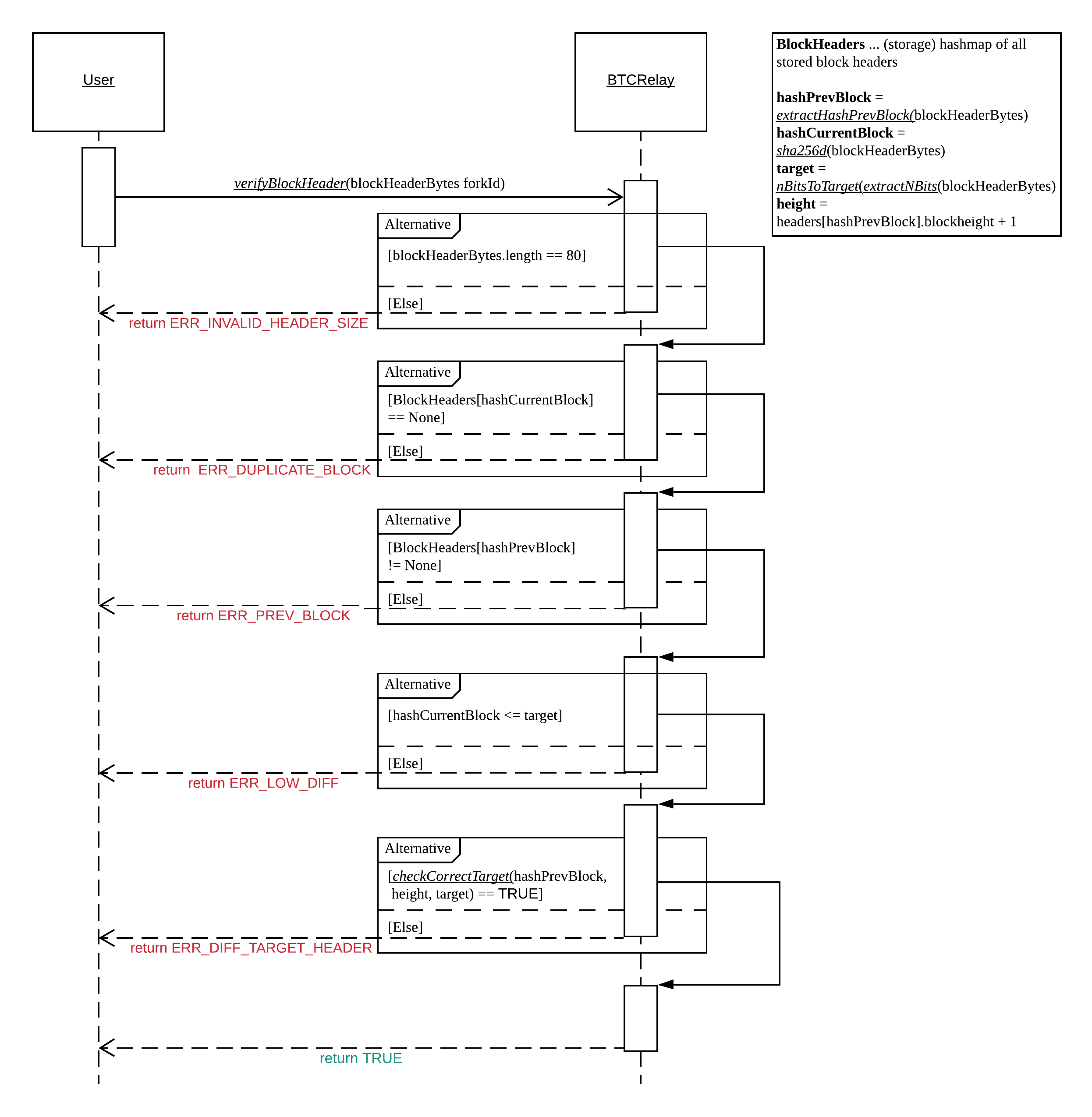
Sequence diagram showing the function sequence of verifyBlockHeader.
verifyTransactionInclusion¶
The verifyTransactionInclusion function is one of the core components of the BTC-Relay: this function checks if a given transaction was indeed included in a given block (as stored in BlockHeaders and tracked by Chains), by reconstructing the Merkle tree root (given a Merkle proof). Also checks if sufficient confirmations have passed since the inclusion of the transaction (considering the current state of the BTC-Relay Chains).
Specification¶
Function Signature
verifyTransactionInclusion(txId, merkleProof, confirmations, insecure)
Parameters
txId: 32 byte hash identifier of the transaction.merkleProof: Merkle tree path (concatenated LE sha256 hashes, dynamic sized).confirmations: integer number of confirmation required.
Note
The Merkle proof for a Bitcoin transaction can be retrieved using the bitcoin-rpc gettxoutproof method and dropping the first 170 characters. The Merkle proof thereby consists of a list of SHA256 hashes, as well as an indicator in which order the hash concatenation is to be applied (left or right).
Returns
True: if the giventxIdappears in at the position specified bytxIndexin the transaction Merkle tree of the block at heightblockHeightand sufficient confirmations have passed since inclusion.- Error otherwise.
Events
VerifyTransaction(txId, txBlockHeight, confirmations): if verification was successful, emit an event specifying thetxId, theblockHeightand the requested number ofconfirmations.
Errors
ERR_SHUTDOWN = "BTC Bridge has shut down": the BTC Bridge has been shutdown by a manual intervention of the Governance Mechanism.ERR_MALFORMED_TXID = "Malformed transaction identifier": return error if the transaction identifier (txId) is malformed.ERR_CONFIRMATIONS = "Transaction has less confirmations than requested": return error if the block in which the transaction specified bytxIdwas included has less confirmations than requested.ERR_INVALID_MERKLE_PROOF = "Invalid Merkle Proof": return error if the Merkle proof is malformed or fails verification (does not hash to Merkle root).ERR_ONGOING_FORK = "Verification disabled due to ongoing fork": return error if themainChainis not at leastSTABLE_BITCOIN_CONFIRMATIONSahead of the next best fork.
Preconditions¶
- The BTC Bridge status must not be set to
SHUTDOWN: 3. IfSHUTDOWNis set, all transaction verification is disabled.
Function Sequence¶
- Check that
txIdis 32 bytes long. ReturnERR_MALFORMED_TXIDerror if this check fails. - Check that the current
BestBlockHeightexceedstxBlockHeightby the requested confirmations. ReturnERR_CONFIRMATIONSif this check fails.
- If
insecure == True, check against user-definedconfirmationsonly- If
insecure == True, check againstmax(confirmations, STABLE_BITCOIN_CONFIRMATIONS).
- Check if the Bitcoin block was stored for a sufficient number of blocks (on the shard) to ensure that staked relayers had the time to flag the block as potentially invalid. Check performed against
STABLE_PARACHAIN_CONFIRMATIONS. - Extract the block header from
BlockHeadersusing theblockHashtracked inChainsat the passedtxBlockHeight. - Check that the first 32 bytes of
merkleProofare equal to thetxIdand the last 32 bytes are equal to themerkleRootof the specified block header. Also check that themerkleProofsize is either exactly 32 bytes, or is 64 bytes or more and a power of 2. ReturnERR_INVALID_MERKLE_PROOFif one of these checks fails. - Call computeMerkle passing
txId,txIndexandmerkleProofas parameters.
- If this call returns the
merkleRoot, emit aVerifyTransaction(txId, txBlockHeight, confirmations)event and returnTrue.- Otherwise return
ERR_INVALID_MERKLE_PROOF.
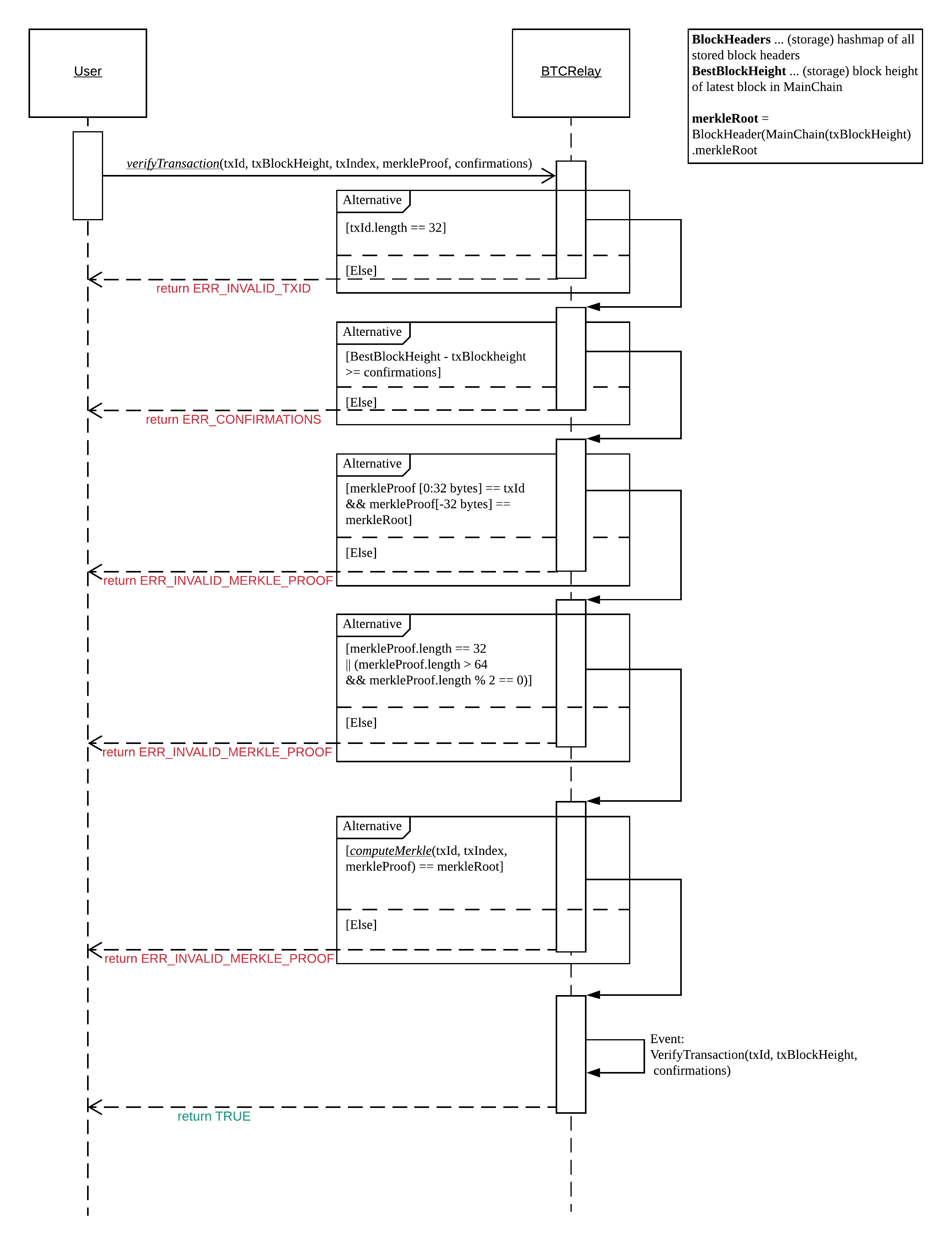
The steps to verify a transaction in the verifyTransactionInclusion function.
validateTransaction¶
Given a raw Bitcoin transaction, this function
- Parses and extracts
- the value and recipient address of the Payment UTXO,
- [Optionally] the OP_RETURN value of the Data UTXO.
- Validates the extracted values against the function parameters.
Note
See Bitcoin Data Model for more details on the transaction structure, and Accepted Bitcoin Transaction Format for the transaction format of Bitcoin transactions validated in this function.
Specification¶
Function Signature
validateTransaction(rawTx, paymentValue, recipientBtcAddress, opReturnId)
Parameters
rawTx: raw Bitcoin transaction including the transaction inputs and outputs.paymentValue: integer value of BTC sent in the (first) Payment UTXO of transaction.recipientBtcAddress: 20 byte Bitcoin address of recipient of the BTC in the (first) Payment UTXO.opReturnId: [Optional] 32 byte hash identifier expected in OP_RETURN (see Replay Attacks).
Returns
True: if the transaction was successfully parsed and validation of the passed values was correct.- Error otherwise.
Events
ValidateTransaction(txId, paymentValue, recipientBtcAddress, opReturnId): if parsing and validation was successful, emit an event specifying thetxId, thepaymentValue, therecipientBtcAddressand theopReturnId.
Errors
ERR_INSUFFICIENT_VALUE = "Value of payment below requested amount": return error the value of the (first) Payment UTXO is lower thanpaymentValue.ERR_TX_FORMAT = "Transaction has incorrect format": return error if the transaction has an incorrect format (see Accepted Bitcoin Transaction Format).ERR_WRONG_RECIPIENT = "Incorrect recipient Bitcoin address": return error if the recipient specified in the (first) Payment UTXO does not match the givenrecipientBtcAddress.ERR_INVALID_OPRETURN = "Incorrect identifier in OP_RETURN field": return error if the OP_RETURN field of the (second) Data UTXO does not match the givenopReturnId.
Preconditions¶
- The BTC Bridge status must not be set to
SHUTDOWN: 3. IfSHUTDOWNis set, all transaction validation is disabled.
Function Sequence¶
See the raw Transaction Format section in the Bitcoin Developer Reference for a full specification of Bitcoin’s transaction format (and how to extract inputs, outputs etc. from the raw transaction format).
- Extract the
outputsfromrawTxusing extractOutputs.
- Extract the value of the Payment UTXO using extractOutputValue and check that it is equal (or greater) than
paymentValue. ReturnERR_INSUFFICIENT_VALUEif this check fails. - Extract the Bitcoin address specified as recipient in the Payment UTXO using extractOutputAddress and check that it matches
recipientBtcAddress. ReturnERR_WRONG_RECIPIENTif this check fails, or the error returned by extractOutputAddress (if the output was malformed). - Extract the OP_RETURN value from the Data UTXO using extractOPRETURN and check that it matches
opReturnId. ReturnERR_INVALID_OPRETURNerror if this check fails, or the error returned by extractOPRETURN (if the output was malformed).
verifyAndValidateTransaction¶
The verifyAndValidateTransaction function is a wrapper around the verifyTransactionInclusion and the validateTransaction functions. It adds an additional check to verify that the validated transaction is the one included in the specified block.
Specification¶
Function Signature
verifyAndValidateTransaction(merkleProof, confirmations, rawTx, paymentValue, recipientBtcAddress, opReturnId)
Parameters
txId: 32 byte hash identifier of the transaction.merkleProof: Merkle tree path (concatenated LE sha256 hashes, dynamic sized).confirmations: integer number of confirmation required.rawTx: raw Bitcoin transaction including the transaction inputs and outputs.paymentValue: integer value of BTC sent in the (first) Payment UTXO of transaction.recipientBtcAddress: 20 byte Bitcoin address of recipient of the BTC in the (first) Payment UTXO.opReturnId: [Optional] 32 byte hash identifier expected in OP_RETURN (see Replay Attacks).
Returns
True: If the same transaction has been verified and validated.- Error otherwise.
Function Sequence¶
- Parse the
rawTxto get the tx id. - Call verifyTransactionInclusion with the applicable parameters.
- Call validateTransaction with the applicable parameters.
flagBlockError¶
Flags tracked Bitcoin block headers when Staked Relayers report and agree on a NO_DATA_BTC_RELAY or INVALID_BTC_RELAY failure.
Attention
This function does not validate the Staked Relayers accusation. Instead, it is put up to a majority vote among all Staked Relayers in the form of a
Note
This function can only be called from the Security module of ONEBTC, after Staked Relayers have achieved a majority vote on a BTC Bridge status update indicating a BTC-Relay failure.
Specification¶
Function Signature
flagBlockError(blockHash, errors)
Parameters
blockHash: SHA256 block hash of the block containing the error.errors: list ofErrorCodeentries which are to be flagged for the block with the given blockHash. Can be “NO_DATA_BTC_RELAY” or “INVALID_BTC_RELAY”.
Events
FlagBTCBlockError(blockHash, chainId, errors)- emits an event indicating that a Bitcoin block hash (identifiedblockHash) in aBlockChainentry (chainId) was flagged with errors (errorslist ofErrorCodeentries).
Errors
ERR_UNKNOWN_ERRORCODE = "The reported error code is unknown": The reportedErrorCodecan only beNO_DATA_BTC_RELAYorINVALID_BTC_RELAY.ERR_BLOCK_NOT_FOUND = "No Bitcoin block header found with the given block hash": NoRichBlockHeaderentry exists with the given block hash.ERR_ALREADY_REPORTED = "This error has already been reported for the given block hash and is pending confirmation": The error reported for the given block hash is currently pending a vote by Staked Relayers.
Function Sequence¶
- Check if
errorscontainsNO_DATA_BTC_RELAYorINVALID_BTC_RELAY. If neither match, returnERR_UNKNOWN_ERRORCODE. - Retrieve the
RichBlockHeaderentry fromBlockHeadersusingblockHash. ReturnERR_BLOCK_NOT_FOUNDif no block header can be found. - Retrieve the
BlockChainentry for the givenRichBlockHeaderusingChainsIndexfor lookup with the block header’schainRefas key. - Flag errors in the
BlockChainentry:- If
errorscontainsNO_DATA_BTC_RELAY, append theRichBlockHeader.blockHeighttoBlockChain.noData - If
errorscontainsINVALID_BTC_RELAY, append theRichBlockHeader.blockHeighttoBlockChain.invalid.
- If
- Emit
FlagBTCBlockError(blockHash, chainId, errors)event, with the givenblockHash, thechainIdof the flaggedBlockChainentry and the givenerrorsas parameters. - Return
clearBlockError¶
Clears ErrorCode entries given as parameters from the status of a RichBlockHeader. Can be NO_DATA_BTC_RELAY or INVALID_BTC_RELAY failure.
Note
This function can only be called from the Security module of ONEBTC, after Staked Relayers have achieved a majority vote on a BTC Bridge status update indicating that a RichBlockHeader entry no longer has the specified errors.
Specification¶
Function Signature
flagBlockError(blockHash, errors)
Parameters
blockHash: SHA256 block hash of the block containing the error.errors: list ofErrorCodeentries which are to be cleared from the block with the given blockHash. Can beNO_DATA_BTC_RELAYorINVALID_BTC_RELAY.
Events
ClearBlockError(blockHash, chainId, errors)- emits an event indicating that a Bitcoin block hash (identifiedblockHash) in aBlockChainentry (chainId) was cleared from the given errors (errorslist ofErrorCodeentries).
Errors
ERR_UNKNOWN_ERRORCODE = "The reported error code is unknown": The reportedErrorCodecan only beNO_DATA_BTC_RELAYorINVALID_BTC_RELAY.ERR_BLOCK_NOT_FOUND = "No Bitcoin block header found with the given block hash": NoRichBlockHeaderentry exists with the given block hash.ERR_ALREADY_REPORTED = "This error has already been reported for the given block hash and is pending confirmation": The error reported for the given block hash is currently pending a vote by Staked Relayers.
Function Sequence¶
- Check if
errorscontainsNO_DATA_BTC_RELAYorINVALID_BTC_RELAY. If neither match, returnERR_UNKNOWN_ERRORCODE. - Retrieve the
RichBlockHeaderentry fromBlockHeadersusingblockHash. ReturnERR_BLOCK_NOT_FOUNDif no block header can be found. - Retrieve the
BlockChainentry for the givenRichBlockHeaderusingChainsIndexfor lookup with the block header’schainRefas key. - Un-flag error codes in the
BlockChainentry.- If
errorscontainsNO_DATA_BTC_RELAY: removeRichBlockHeader.blockHeightfromBlockChain.noData - If
errorscontainsINVALID_BTC_RELAY: removeRichBlockHeader.blockHeightfromBlockChain.invalid
- If
- Emit
ClearBlockError(blockHash, chainId, errors)event, with the givenblockHash, thechainIdof the flaggedBlockChainentry and the givenerrorsas parameters. - Return